How hard is it to prevent recurring blackouts in Puerto Rico?
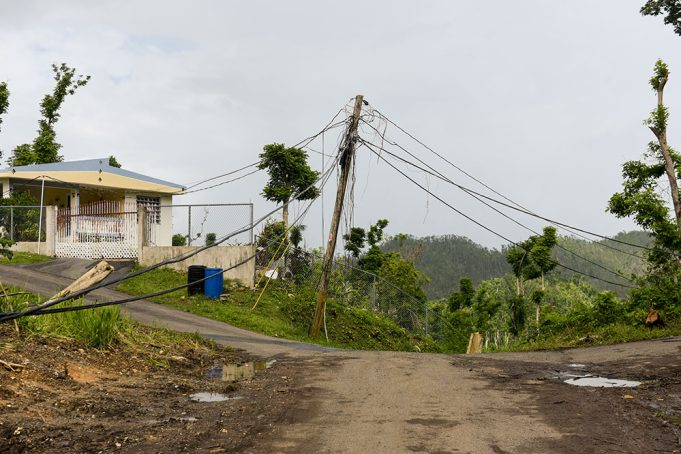

Using the island as a model, researchers demonstrate the “DyMonDS” framework can improve resiliency to extreme weather and ease the integration of new resources.
Researchers at MIT’s Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems (LIDS) have shown that using decision-making software and dynamic monitoring of weather and energy use can significantly improve resiliency in the face of weather-related outages, and can also help to efficiently integrate renewable energy sources into the grid.
The researchers point out that the system they suggest might have prevented or at least lessened the kind of widespread power outage that Puerto Rico experienced last week by providing analysis to guide rerouting of power through different lines and thus limit the spread of the outage.
The computer platform, which the researchers describe as DyMonDS, for Dynamic Monitoring and Decision Systems, can be used to enhance the existing operating and planning practices used in the electric industry. The platform supports interactive information exchange and decision-making between the grid operators and grid-edge users — all the distributed power sources, storage systems and software that contribute to the grid. It also supports optimization of available resources and controllable grid equipment as system conditions vary. It further lends itself to implementing cooperative decision-making by different utility- and non-utility-owned electric power grid users, including portfolios of mixed resources, users, and storage. Operating and planning the interactions of the end-to-end high-voltage transmission grid with local distribution grids and microgrids represents another major potential use of this platform.
This general approach was illustrated using a set of publicly-available data on both meteorology and details of electricity production and distribution in Puerto Rico. An extended AC Optimal Power Flow software developed by SmartGridz Inc. is used for system-level optimization of controllable equipment. This provides real-time guidance for deciding how much power, and through which transmission lines, should be channeled by adjusting plant dispatch and voltage-related set points, and in extreme cases, where to reduce or cut power in order to maintain physically-implementable service for as many customers as possible. The team found that the use of such a system can help to ensure that the greatest number of critical services maintain power even during a hurricane, and at the same time can lead to a substantial decrease in the need for construction of new power plants thanks to more efficient use of existing resources.
The findings are described in a paper in the journal Foundations and Trends in Electric Energy Systems, by MIT LIDS researchers Marija Ilic and Laurentiu Anton, along with recent alumna Ramapathi Jaddivada.
“Using this software,” Ilic says, they show that “even during bad weather, if you predict equipment failures, and by using that information exchange, you can localize the effect of equipment failures and still serve a lot of customers, 50 percent of customers, when otherwise things would black out.”
Anton says that “the way many grids today are operated is sub-optimal.” As a result, “we showed how much better they could do even under normal conditions, without any failures, by utilizing this software.” The savings resulting from this optimization, under everyday conditions, could be in the tens of percents, they say.
The way utility systems plan currently, Ilic says, “usually the standard is that they have to build enough capacity and operate in real time so that if one large piece of equipment fails, like a large generator or transmission line, you still serve customers in an uninterrupted way. That’s what’s called N-minus-1.” Under this policy, if one major component of the system fails, they should be able to maintain service for at least 30 minutes. That system allows utilities to plan for how much reserve generating capacity they need to have on hand. That’s expensive, Ilic points out, because it means maintaining this reserve capacity all the time, even under normal operating conditions when it’s not needed.
In addition, “right now there are no criteria for what I call N-minus-K,” she says. If bad weather causes five pieces of equipment to fail at once, “there is no software to help utilities decide what to schedule” in terms of keeping the most customers, and the most important services such as hospitals and emergency services, provided with power. They showed that even with 50 percent of the infrastructure out of commission, it would still be possible to keep power flowing to a large proportion of customers.
Their work on analyzing the power situation in Puerto Rico started after the island had been devastated by hurricanes Irma and Maria. Most of the electric generation capacity is in the south, yet the largest loads are in San Juan, in the north, and Mayaguez in the west. When transmission lines get knocked down, a lot of rerouting of power needs to happen quickly.
With the new systems, “the software finds the optimal adjustments for set points,” for example, changing voltages can allow for power to be redirected through less-congested lines, or can be increased to lessen power losses, Anton says.
The software also helps in the long-term planning for the grid. As many fossil-fuel power plants are scheduled to be decommissioned soon in Puerto Rico, as they are in many other places, planning for how to replace that power without having to resort to greenhouse gas-emitting sources is a key to achieving carbon-reduction goals. And by analyzing usage patterns, the software can guide the placement of new renewable power sources where they can most efficiently provide power where and when it’s needed.
As plants are retired or as components are affected by weather, “We wanted to ensure the dispatchability of power when the load changes,” Anton says, “but also when crucial components are lost, to ensure the robustness at each step of the retirement schedule.”
One thing they found was that “if you look at how much generating capacity exists, it’s more than the peak load, even after you retire a few fossil plants,” Ilic says. “But it’s hard to deliver.” Strategic planning of new distribution lines could make a big difference.
Jaddivada, director of innovation at SmartGridz, says that “we evaluated different possible architectures in Puerto Rico, and we showed the ability of this software to ensure uninterrupted electricity service. This is the most important challenge utilities have today. They have to go through a computationally tedious process to make sure the grid functions for any possible outage in the system. And that can be done in a much more efficient way through the software that the company developed.”
The project was a collaborative effort between the MIT LIDS researchers and others at MIT Lincoln Laboratory, the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, with overall help of SmartGridz software.